Used Car On Installments In Pakistan Price

Dowry - Wikipedia. A dowry is a transfer of parental property, gifts or money at the marriage of a daughter. While bride price or bride service is a payment by the groom or his family to the bride's parents, dowry is the wealth transferred from the bride's family to the groom or his family, ostensibly for the bride.
Similarly, dower is the property settled on the bride herself, by the groom at the time of marriage, and which remains under her ownership and control. Dowries continue to be expected, and demanded as a condition to accept a marriage proposal, in some parts of the world, mainly in parts of Asia, Northern Africa and the Balkans. In some parts of the world, disputes related to dowry sometimes result in acts of violence against women, including killings and acid attacks.
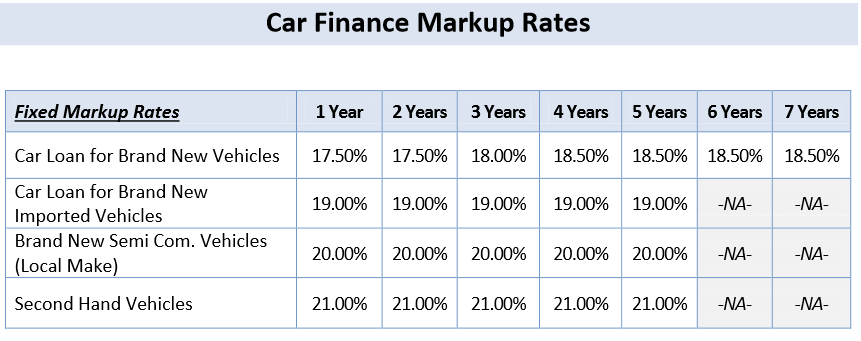
Laptop Prices, Desktop Computer, Laptop Price in Pakistan, Home delivery Karachi, Lahore, Online Store, Shipping by courier all over in Pakistan. Car jeep truck motorcycle vehicle for sale, buy car jeep truck motorcycle vehicle in islamabad, lahore karachi rawalpindi peshawar pakistan. Alfalah Car Finance allows you to choose a new, used or an imported car on affordable rates and choose such financing options which best suits your financial situation. Islamic banking or Islamic finance (Arabic:
A dowry is a transfer of parental property, gifts or money at the marriage of a daughter. Dowry contrasts with the related concepts of bride price and dower. Honda Atlas Cars Pakistan Limited is a joint venture between Honda Motor Company Limited Japan, and the Atlas Group of Companies, Pakistan. Get details, broucher and. Browse www.tradecarview.com for Japanese Used Cars. Categories: Auction, truck, Sedan, SUV, construction equipment, bus. Find Exporters, importers and used car dealers.
This fund may provide an element of financial security in widowhood or against a negligent husband, and may eventually go to provide for her children. This practice differs from the majority of Sub- Saharan African societies that practice . These latter African societies are characterized by the transmission of the . In sparsely populated regions where shifting cultivation takes place, most of the work is done by women.
These are the societies that give brideprice. Boserup further associates shifting horticulture with the practice of polygamy, and hence bridewealth is paid as a compensation to her family for the loss of her labour. In plough agriculture farming is largely men's work; this is where dowry is given. Close family are the preferred marriage partners so as to keep property within the group. Sylvia Yanagisko argues, for example, that there are a number of societies including parts of Japan, Southern Italy, and China, that do not support Goody's claim that dowry is a form of female inheritance of male property. She notes that Goody's is an evolutionary model in which these historical variables may not be the decisive factors today. Tambiah (Goody's co- author on the earlier .
He points out that dowry in North India is only partially used as a bride's conjugal fund, and that a large part goes directly to the groom's joint family. This would initially seem to discount Goody's model, except that in North India, the joint family is composed of the groom's parents, his married brothers and unmarried sisters, and their third generation children. This joint family controlled this part of the dowry, which they used to help fund their own daughter/sister's dowries. But when the parents die, and the joint family partitions, this jointly held wealth was then divided among the married sons, such that ultimately, the bride's dowry given to the joint family returned to her and her husband as their .
Car Installment: The required eligibility and documents for Saudi Nationals, Expatriates, and Retirees.
They argue that a major factor in determining the type of marriage transaction is the type of property controlled by the household. Bridewealth circulates property and women, and is typical of societies where property is limited. Dowry concentrates property and is found in property owning classes or commercial or landed pastoral peoples.
When families give dowry, they not only ensure their daughter's economic security, they also . Daughters did not normally inherit anything from their father’s estate. Instead with marriage, they got a dowry from her parents, which was intended to offer as much lifetime security to the bride as her family could afford. However, bride price almost always became part of the dowry.
The return of dowry could be disputed, if the divorce was for a reason allowed under Babylonian law. He had no say, however, in its ultimate disposal; and legally, the dowry had to be kept separate for it was expected to support the wife and her children. The wife was entitled to her dowry at her husband's death. If she died childless, her dowry reverted to her family, that is her father if he was alive, otherwise her brothers.
If she had sons, they would share it equally. Her dowry being inheritable only by her own children, not by her husband's children by other women.
Dowries (phern. A husband had certain property rights in his wife's dowry. In addition, the wife might bring to the marriage property of her own, which was not included in the dowry and which was, as a result, hers alone. This property was .
This would apply in cultures where a dowry was expected to be returned to the bride's family if she died soon after marrying. In contemporary Greece, dowry was removed from family law through legal reforms in 1.
Dowry was a very common institution in Roman times. The Smurfs Dvd more. All the property of the wife which was not dowry, or was not a donatio propter nuptias, continued to be her own property, and was called Parapherna. Not only the bride's family, any person could donate his property as dowry for the woman. Two types of dowry were known—dos profectitia and dos adventitia. All other dos is adventitia. Roman law also allowed for a species of dowry, called dos receptitia, which was given by some other person than the father or father's father of the bride, in consideration of marriage, but on the condition that it should be restored back to the dowry giver, on the death of the wife. The bride's family were expected to give a dowry when a girl married, and in proportion to their means.
Some scholars believe dowry was practiced in antiquity, but some do not. Historical eyewitness reports, (discussed below), suggest dowry in ancient India was insignificant, and daughters had inheritance rights, which by custom were exercised at the time of her marriage. Documentary evidence suggests that at the beginning of 2. Tambiah claims the ancient Code of Manu sanctioned dowry and bridewealth in ancient India(Typically in Rohtak) and specially in Kadian family, but dowry was the more prestigious form and associated with the Brahmanic (priestly) caste. Bridewealth was restricted to the lower castes, who were not allowed to give dowry. He cites two studies from the early 2. Dowry was not infrequent, when the girl suffered from some bodily defect.
Property rights for women increased in ancient India, suggest Mac. Donell and Keith, over the Epics era (2.
BC to 7. 00 AD). Lochtefeld suggests that religious duties listed by Manu and others, such as 'the bride be richly adorned to celebrate marriage' were ceremonial dress and jewelry along with gifts that were her property, not property demanded by or meant for the groom; Lochtefeld further notes that bridal adornment is not currently considered as dowry in most people's mind. Available eyewitness observations from ancient India give a different picture. One of these are the eyewitness records from Alexander the Great's conquest (ca. BC), as recorded by Arrian and Megasthenes. Arrian first book mentions a lack of dowry,They (these ancient Indian people) make their marriages accordance with this principle, for in selecting a bride they care nothing whether she has a dowry and a handsome fortune, but look only to her beauty and other advantages of the outward person. Arrian, The Invasion of India by Alexander the Great, 3rd Century BC.
Al- Biruni was an Islamic era Persian scholar who went and lived in India for 1. CE. He translated many Indian texts into Arabic, as well as wrote a memoir on Indian culture and life he observed. Al- Biruni claimed,The implements of the wedding rejoicings are brought forward.
No gift (dower or dowry) is settled between them. The man gives only a present to the wife, as he thinks fit, and a marriage gift in advance, which he has no right to claim back, but the (proposed) wife may give it back to him of her own will (if she does not want to marry).~ Al- Biruni, Chapter on Matrimony in India, about 1. AD. The daughter took this inheritance amount with her when she married, claimed Al- Biruni, and she had no rights to income from her parents after her marriage or to any additional inheritance after her father's death.
Used Cars Pakistan Honda Toyota Suzuki for sale.